Research | Departments
Research
Departments
Research | Departments
Research
Departments
Molecular Oncology, Anti-cancer Drug Development, Translational Laboratory Science

Email | d002089002@tmu.edu.tw
Profile | Academic Hub/Pure Experts
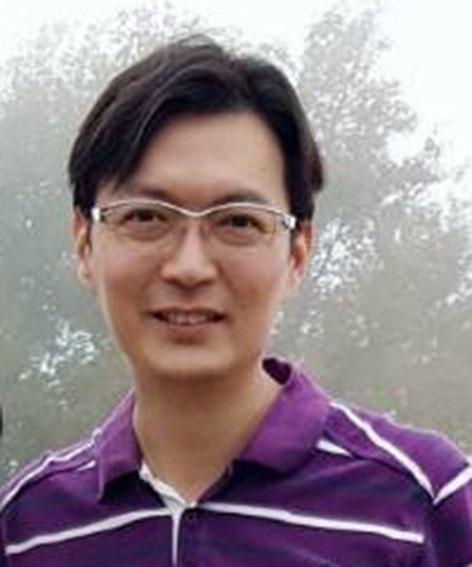
Professor (Ph.D.)
Cancer biology, Cancer Molecular Medicine, Cancer Treatment Resistance
Laboratory of Molecular Oncology and Anticancer Drug Development
–
–
–
–
–
Assoc. Prof.
Assoc. Prof.
Assoc. Prof.
Assoc. Prof.
Assoc. Prof.
Assoc. Prof.
Research Fellow
Research Fellow
MD, PhD
MD, PhD Student
PhD Student
Research Assist.
Research Assist.
Research Assist.
Research Assist.
Yang YC, Lin YW, Lee WJ, Lai FR, Ho KH, Chu CY, Hua KT, Chen JQ, Tung MC, Hsiao M, Wen YC*, Chien MH*.
The RNA-binding protein KSRP aggravates malignant progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through transcriptional inhibition and post-transcriptional destabilization of the NEDD4L ubiquitin ligase.
J Biomed Sci. 2023 30(1):68 (*correspondence) (IF:11; Ranking:11/139; 7.9 %)
Abstract
–
Yang YC, Pan KF, Lee WJ, Chang JH, Tan P, Gu CC, Chang WM, Yang SF, Hsiao M, Hua KT, Chien MH*.
Circulating proteoglycan endocan mediates EGFR-driven progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res.
2020 80(16):3292-3304. (*correspondence) (IF:11.2; Ranking:26/241; 10.8%).
Abstract
–
Wen YC, Lin YW, Chu CY, Yang YC, Yang SF, Liu YF, Hsiao M, Lee WJ, Chien MH*.
Melatonin-triggered post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications of ADAMTS1 coordinately retard tumorigenesis and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma.
J Pineal Res. 2020 69(2):e12668 (*correspondence) (IF:10.3; Ranking:3/79; 8.3%).
Abstract
A disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTS) family are widely implicated in tissue remodeling events manifested in cancer development. ADAMTS1, the most fully characterized ADAMTS, plays conflicting roles in different cancer types; however, the role of ADAMTS1 in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) remains unclear. Herein, we found that ADAMTS1 is highly expressed in RCC tissues compared to normal renal tissues, and its expression was correlated with an advanced stage and a poor prognosis of RCC patients. In vitro, we observed higher expression of ADAMTS1 in metastatic (m)RCC cells compared to primary cells, and manipulation of ADAMTS1 expression affected cell invasion and clonogenicity. Results from protease array showed that ADAMTS1 is modulated by melatonin through mechanisms independent of the MT1 receptor in mRCC cells, and overexpression of ADAMTS1 relieved the invasion/clonogenicity and growth/metastasis inhibition imposed by melatonin treatment in vitro and in an orthotopic xenograft model. The human microRNA (miR) OneArray showed that miR-181d and miR-let-7f were induced by melatonin and, respectively, targeted the 3’-UTR and non-3′-UTR of ADAMTS1 to suppress its expression and mRCC invasive ability. Clinically, RCC patients with high levels of miR-181d or miR-let-7f and a low level of ADAMTS1 had the most favorable prognoses. In addition, ubiquitin/proteasome-mediated degradation of ADAMTS1 can also be triggered by melatonin. Together, our study indicates that ADAMTS1 may be a useful biomarker for predicting RCC progression. The novel convergence between melatonin and ADAMTS1 post-transcriptional and post-translational regulation provides new insights into the role of melatonin-induced molecular regulation in suppressing RCC progression.
Chien MH, Lin YW, Wen YC, Yang YC, Hsiao M, Chang JL, Huang HC, Lee WJ.
Targeting the SPOCK1-snail/slug axis-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by apigenin contributes to repression of prostate cancer metastasis.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 38(1):246. (First author) (IF:11.3; Ranking:25/241; 10.4%)
Abstract
Abstract Background Prostate cancer (PCa) is considered one of the most prevalent malignancy globally, and metastasis is a major cause of death. Apigenin (API) is a dietary flavonoid which exerts an antimetastatic effect in various cancer types. Sparc/osteonectin, cwcv, and kazal-like domains proteoglycan 1 (SPOCK1) is a crucial modulator of tumor growth and metastasis in cancers. However, the role and underlying regulatory mechanisms of SPOCK1 in the API-mediated antimetastatic effects of PCa remain unclear. Methods MTS, colony formation, wound-healing, and transwell assays were conducted to evaluate the effects of API on PCa cell proliferative, migratory, and invasive potentials. In vivo orthotopic bioluminescent xenograft model were employed to determine antitumor activity of API. PCa cells were transfected with either Snail-, Slug-, SPOCK1-overexpressing vector, or small hairpin (sh)SPOCK1 to determine the invasive abilities and expression levels of SPOCK1 and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) biomarkers in response to API treatment. Immunohistochemical (IHC) assays were carried out to evaluate the expression level of SPOCK1 in PCa xenografts and a PCa tissue array. Associations of SPOCK1 expression with clinicopathological features and prognoses of patients with PCa were analyzed by GEO or TCGA RNA-sequencing data. Results API significantly suppressed in vitro PCa cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and inhibited in vivo PCa tumor growth and metastasis. Moreover, survival times of animals were also prolonged after API treatment. Mechanistic studies revealed that API treatment resulted in downregulation of SPOCK1, which was accompanied by reduced expressions of mesenchymal markers and subsequent attenuation of invasive abilities of PCa cells. Overexpression of SPOCK1 in PCa xenografts resulted in significant promotion of tumor progression and relieved the anticancer activities induced by API, whereas knockdown of SPOCK1 had opposite effects. In clinical, SPOCK1 levels were higher in tumor tissues compared to non-tumor tissues, which was also significantly correlated with shorter disease-free survival in PCa patients. Conclusions Levels of SPOCK1 increase with the progression of human PCa which suggests that SPOCK1 may act as a prognostic marker or therapeutic target for patients with PCa. Suppression of SPOCK1-mediated EMT signaling contributes to the antiproliferative and antimetastatic activities of API in vitro and in vivo.
Chen MW#, Yang ST#, Chien MH#, Hua KT, Wu CJ, Hsiao SM, Lin H, Hsiao M, Su JL, Wei LH.
The STAT3-miRNA-92-Wnt signaling pathway regulates spheroid formation and malignant progression in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
2017 77:1955-1967 (#equal contribution) (IF:11.2; Ranking:26/241; 10.8%).
Abstract
Accumulating evidence has shown that Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) is thought to be a promising target for cancer therapy as STAT3 is frequently overexpressed in a wide range of cancer cells as well as clinical specimens, promoting tumor progression. It is widely accepted that STAT3 regulates a variety of cellular processes, such as tumor cell growth, survival, invasion, cancer stem cell-like characteristic, angiogenesis and drug-resistance. In this review, we focus on the role of STAT3 in tumorigenesis in ovarian cancer and discuss the existing inhibitors of STAT3 signaling that can be promisingly developed as the strategies for ovarian cancer therapy.
Lin YW, Lee LM, Lee WJ, Chu CY, Tan P, Yang YC, Chen WY, Yang SF, Hsiao M, Chien MH*.
Melatonin inhibits MMP-9 transactivation and renal cell carcinoma metastasis by suppressing Akt-MAPKs pathway and NF-κB-DNA- binding activity.
J Pineal Res. 2016 60(3):277-90 (*correspondence) (IF:10.3; Ranking:3/79; 3.8 %).
Abstract
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most lethal of all urological malignancies because of its potent metastasis potential. Melatonin exerts multiple tumor-suppressing activities through antiproliferative, proapoptotic, and anti-angiogenic actions and has been tested in clinical trials. However, the antimetastastic effect of melatonin and its underlying mechanism in RCC are unclear. In this study, we demonstrated that melatonin at the pharmacologic concentration (0.5-2 mm) considerably reduced the migration and invasion of RCC cells (Caki-1 and Achn). Furthermore, we found that melatonin suppressed metastasis of Caki-1 cells in spontaneous and experimental metastasis animal models. Mechanistic investigations revealed that melatonin transcriptionally inhibited MMP-9 by reducing p65- and p52-DNA-binding activities. Moreover, the Akt-mediated JNK1/2 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways were involved in melatonin-regulated MMP-9 transactivation and cell motility. Clinical samples revealed an inverse correlation between melatonin receptor 1A (MTNR1A) and MMP-9 expression in normal kidney and RCC tissues. In addition, a higher survival rate was found in MTNR1Ahigh/MMP-9low patients than in MTNR1Alow/MMP-9high patients. Overall, our results provide new insights into the role of melatonin-induced molecular regulation in suppressing RCC metastasis and suggest that melatonin has potential therapeutic applications for metastastic RCC.
Chien MH, Lee WJ, Hsieh FK, Li CF, Cheng TY, Wang MY, Chen JS, Chow JM, Jan YH, Hsiao M, Hua KT, Kuo ML.
Keap1-Nrf2 interaction suppresses cell motility in lung adenocarcinomas by targeting the S100P protein.
Clin Cancer Res. 2015 21(20):4719-32 (First author) (IF:11.5; Ranking:22/241; 9.1 %).
Abstract
Purpose: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) is an E3 ligase participated in the cellular defense response against oxidative stress through nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). However, the role of Keap1 in regulating cancer motility is still controversial. We investigated the contribution of the Keap1-Nrf2 axis in the progression of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Experimental Design: The expression of Keap1 and Nrf2 was examined via immunohistochemistry, real-time PCR, and Western blot analysis in a cohort of NSCLC tissues and cells. A series of in vivo and in vitro assays was performed to elucidate the contribution of the Keap1-Nrf2 axis in lung cancer mobility and progression. Results: Keap1 expression was decreased in specimens from NSCLC patients with lymph node metastasis compared with patients without metastasis. Higher Keap1 expression levels were correlated with the survival of NSCLC patients. Moreover, manipulation of Keap1 expression affected cell migration/invasion abilities. Depletion of Nrf2 relieved the migration promotion imposed by Keap1 suppression. Mechanistic investigations found that S100P was downregulated in both Keap1-overexpressing and Nrf2-knockdown NSCLC cells. Overexpression of Keap1 and knockdown of Nrf2 both suppressed S100P expression in NSCLC cells. Knockdown of S100P inhibited cell migration in highly invasive NSCLC cells and also relieved the migration promotion imposed by Keap1 suppression in weakly invasive NSCLC cells. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that Keap1 functions as a suppressor of tumor metastasis by targeting the Nrf2/S100P pathway in NSCLC cells. In addition, overexpression of Keap1 may be a novel NSCLC treatment strategy and/or useful biomarker for predicting NSCLC progression.

 Total Users : 362557
Total Users : 362557
 Chao-Wen Cheng
Chao-Wen Cheng 